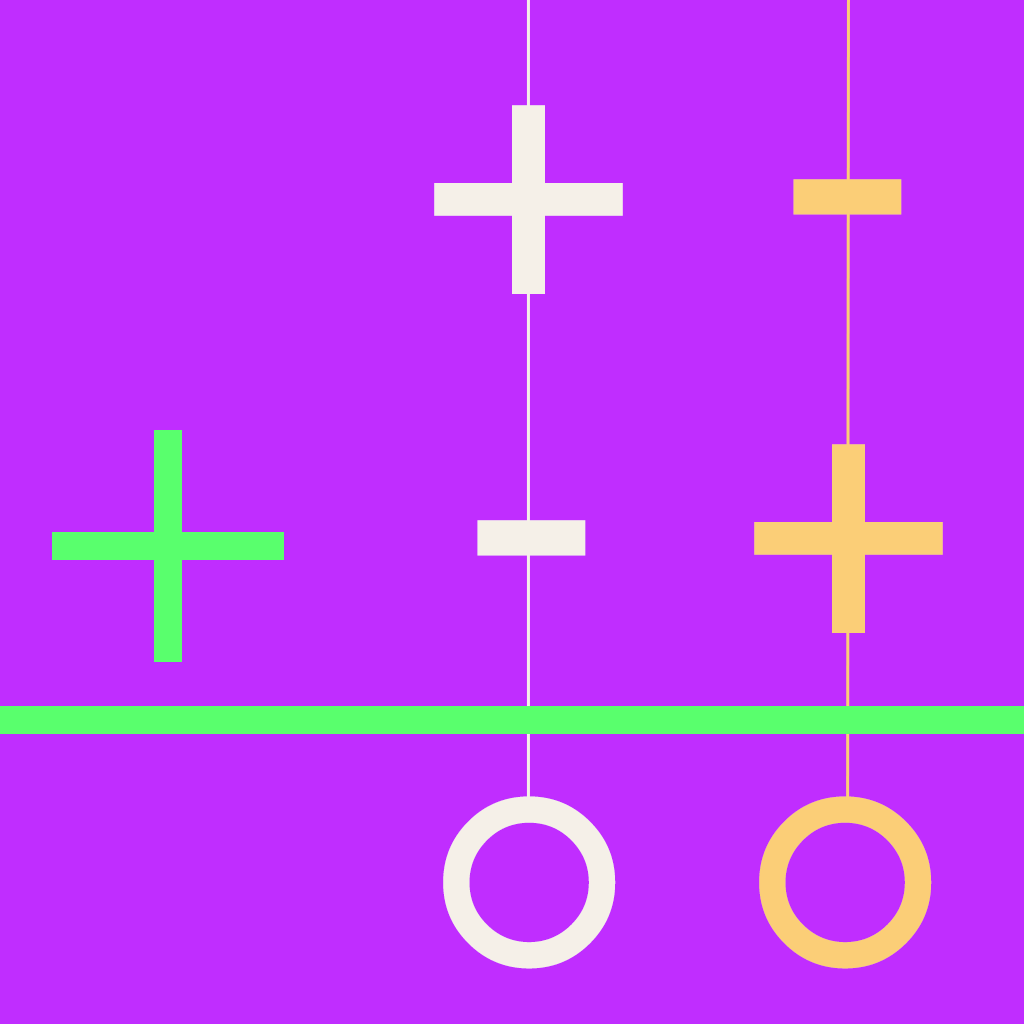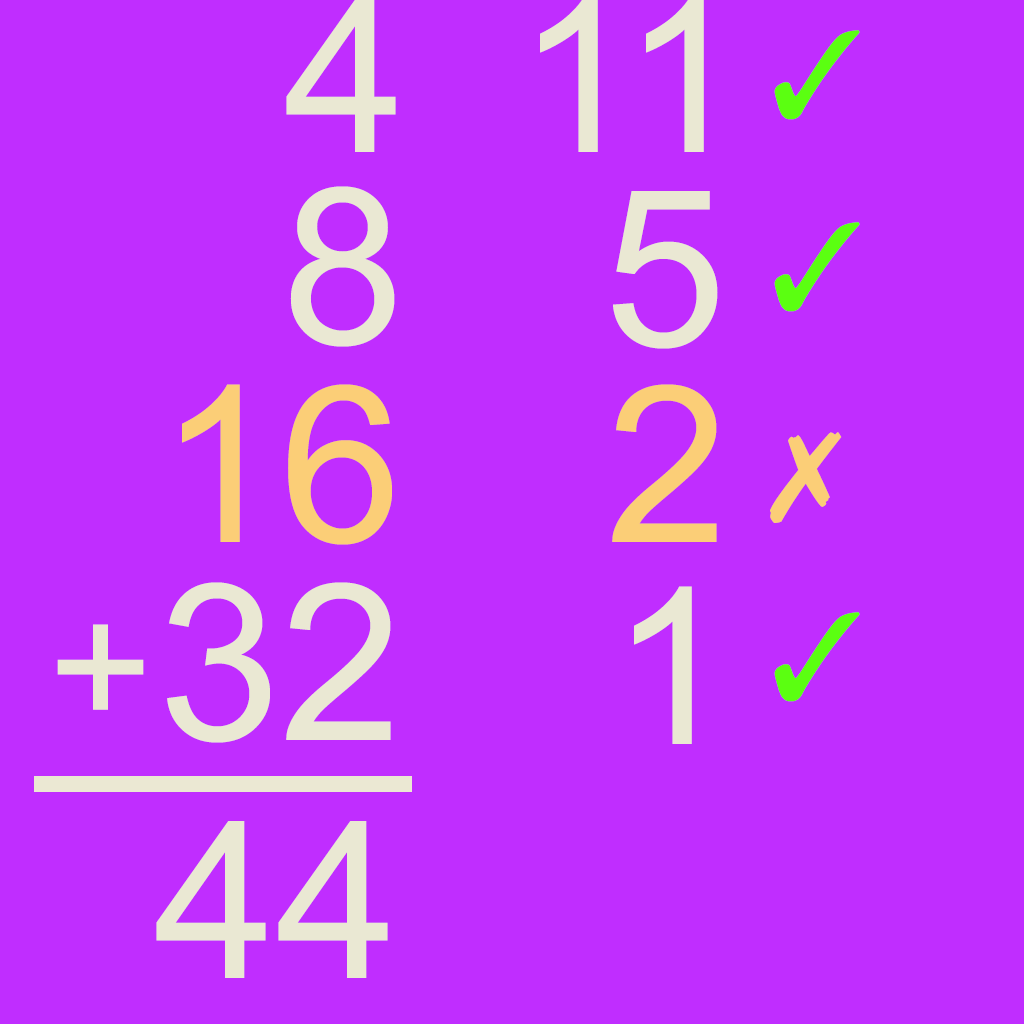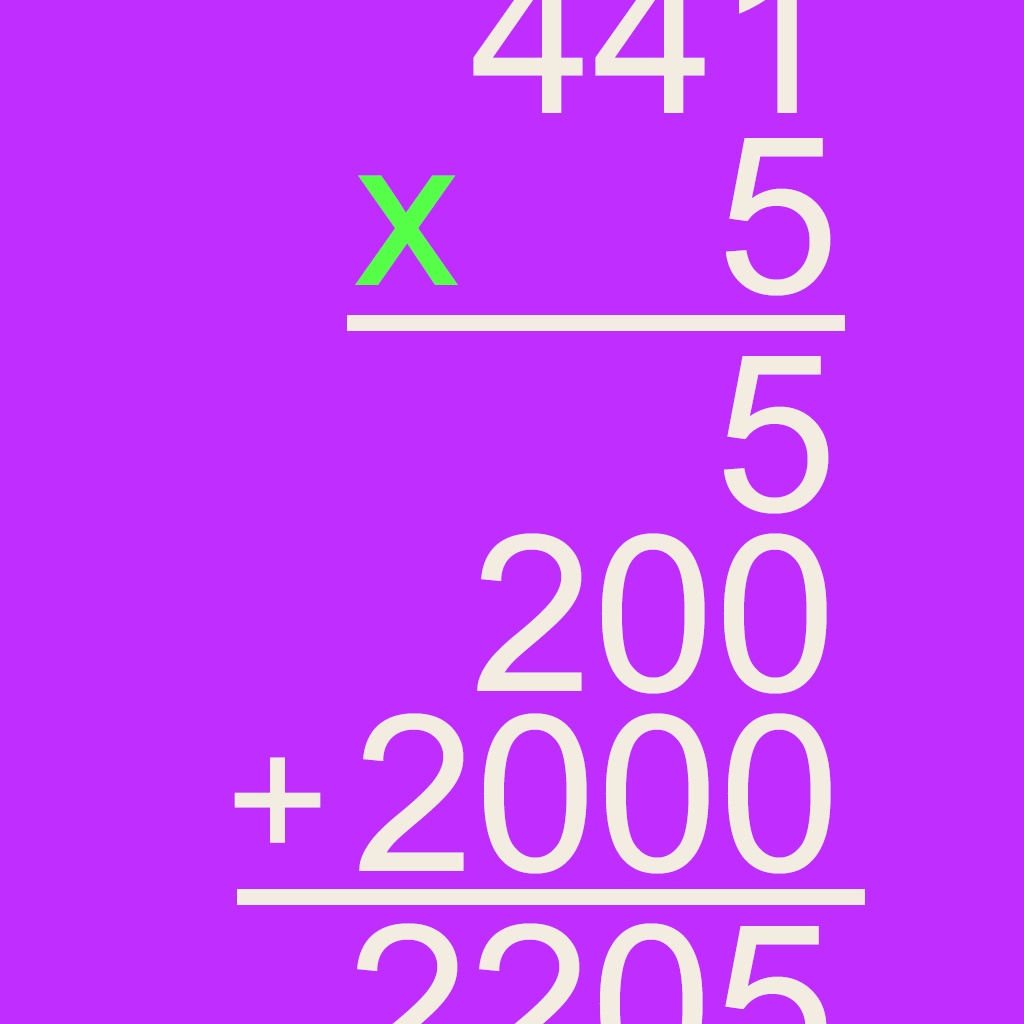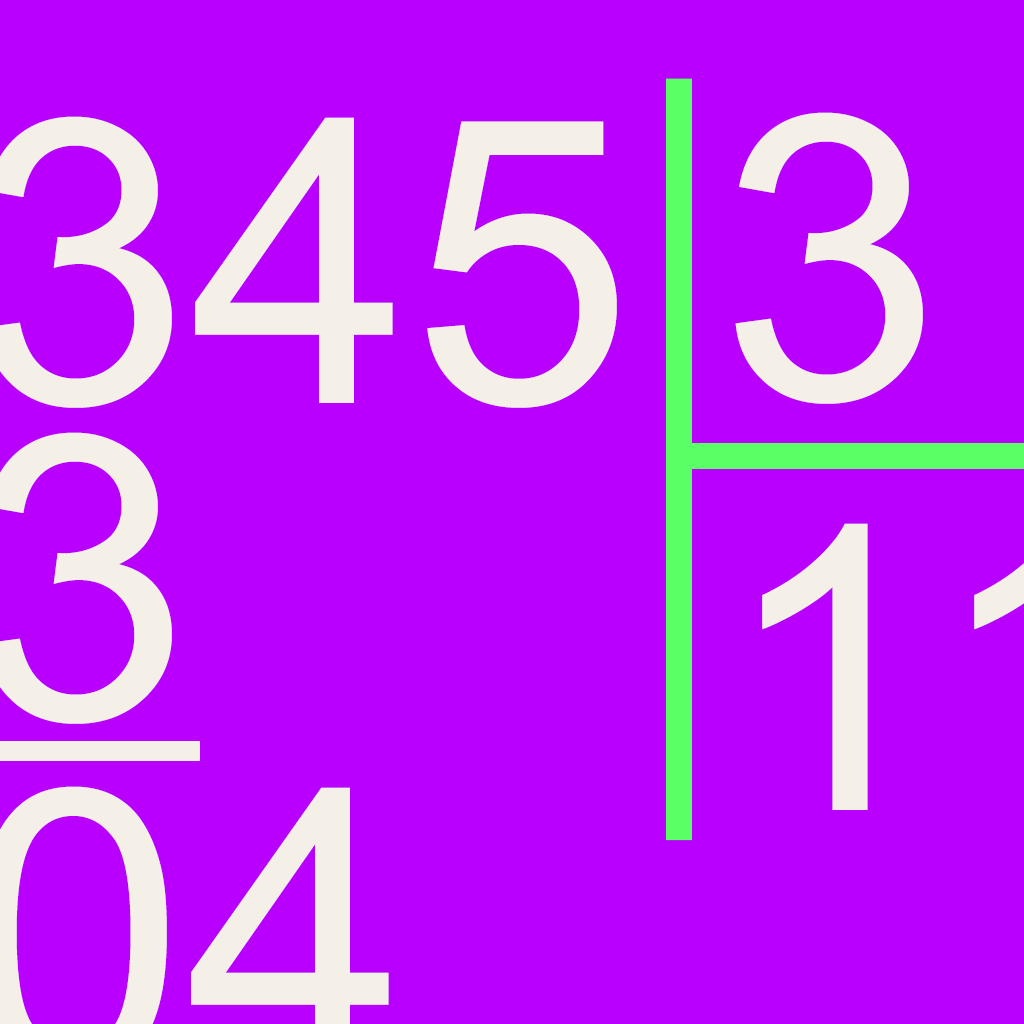Alternative Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction Algorithms Bundle
45
ASO score
Text
40/100
Reviews
50/100
Graphic
60/100
Other
0/100
App Rating
4
Votes
1
App Age
Last Update
Compare with Category Top Apps
|
Metrics
|
Current App
|
Category Top Average
|
Difference
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Rating
|
4
|
4.56
|
-12%
|
|
Number of Ratings (Voted)
|
1
|
3M
|
-100%
|
|
App Age
|
0y 0m
|
6y 6m
|
|
|
Price
|
$15
|
$0
|
|
|
In-app Purchases Price
|
$0
|
$20
|
|
|
Update Frequency
|
0d
|
34d
|
|
|
Title Length
|
81
|
17
|
+376%
|
|
Subtitle Length
|
0
|
24
|
|
|
Description Length
|
3 923
|
2 176
|
+80%
|
|
Number of Screenshots
|
780
|
1277
|
-39
%
|
|
Size
|
0MB
|
813MB
|
|
Category Ranking in United States
7 days
Last 7 days
Last 30 days
Last 90 days
Last 180 days
Last year
| Top | Dec 01, 2025 | Dec 08, 2025 |
|---|---|---|
|
No results were found!
|
||
| Top | Dec 01, 2025 | Dec 08, 2025 |
|---|---|---|
|
No results were found!
|
||
| Top | Dec 01, 2025 | Dec 08, 2025 |
|---|---|---|
|
No results were found!
|
||
| Top | Dec 01, 2025 | Dec 08, 2025 |
|---|---|---|
|
No results were found!
|
||
Ranking Keywords in United States
| Keywords | App Rank |
|---|

Analyze this and other apps using Asolytics tools
Text ASO
Title
(
Characters:
81
of 30
)
Alternative Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction Algorithms Bundle
Subtitle
(
Characters:
0
of 30
)
Description
(
Characters:
3923
of 4000
)
This bundle has 10 iDevBooks math apps. Save 62% compared to buying the apps separately.
Lattice Multiplication
Lattice multiplication is algorithmically equivalent to long multiplication. A lattice (a grid) guides the calculation. All the multiplications are done first and then the additions. The method was introduced to Europe in 1202 in Fibonacci's Liber Abaci.
In this groundbreaking book Fibonacci presented many algorithms for working with Arabic numerals. Ancient Indians and Chinese originally invented some of the algorithms. Fibonacci presented both the current standard long multiplication and also an originally Indian method called lattice multiplication, which is faster and more compact for working with larger numbers.
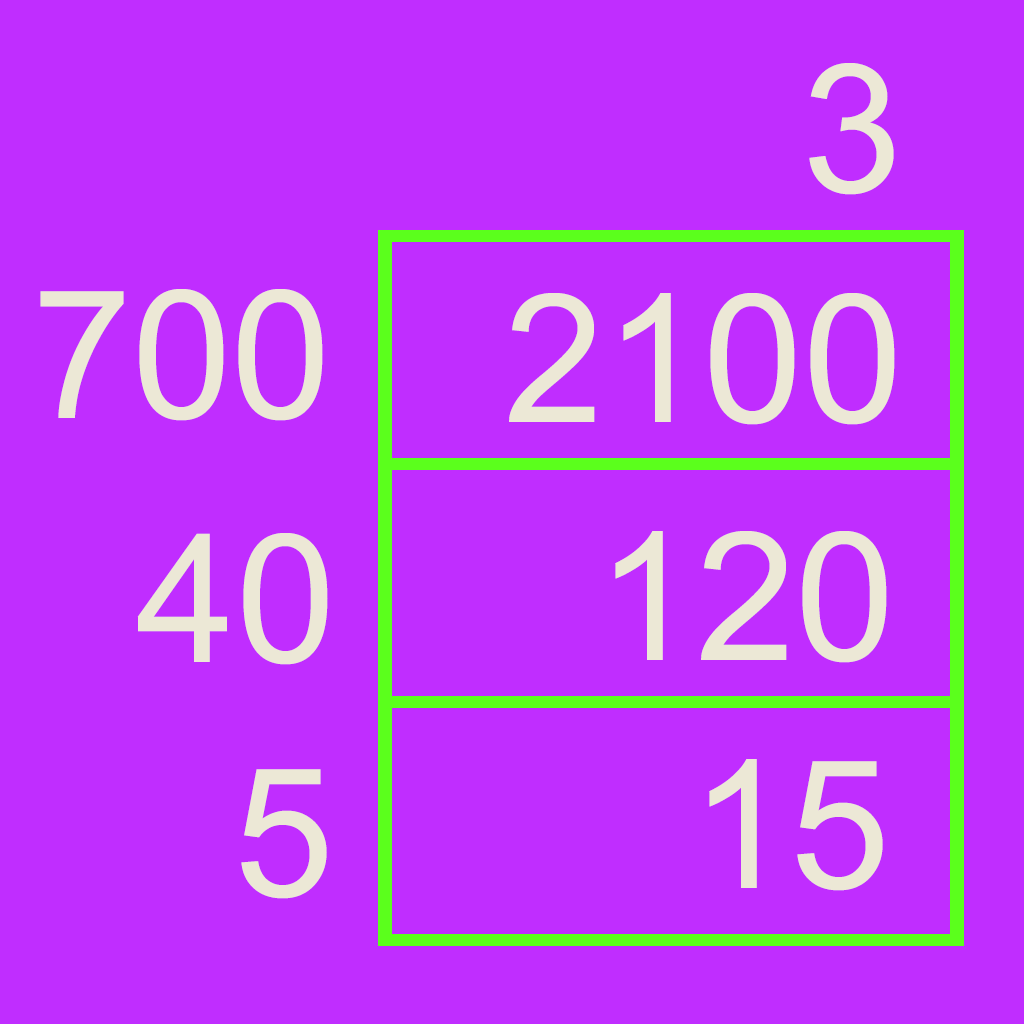
Grid Multiplication
The grid multiplication method is a two-step process. In the example 39 x 24 the numbers are first broken up into 30 + 9 and 20 + 4, and written on a grid. Multiplying the row and column headers then solves each cell of the grid. Eventually the partial products 600, 180, 120, and 36 are added together.
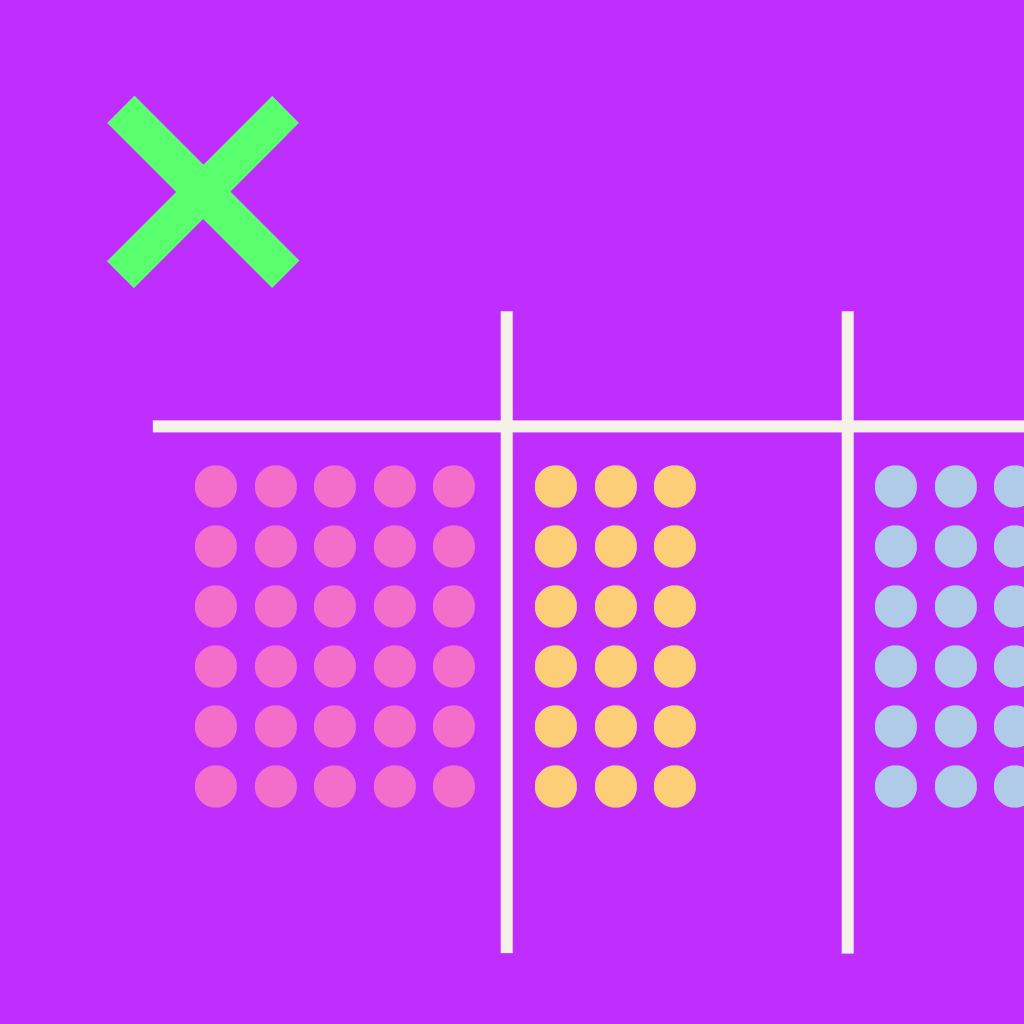
Egyptian Multiplication
Ancient Egyptians were able to multiply any two numbers by using just the ability to multiply by 2, and to add.
Russian Multiplication
In this method is the the only multiplication facts we need to know are how to double and how to take half of a number.
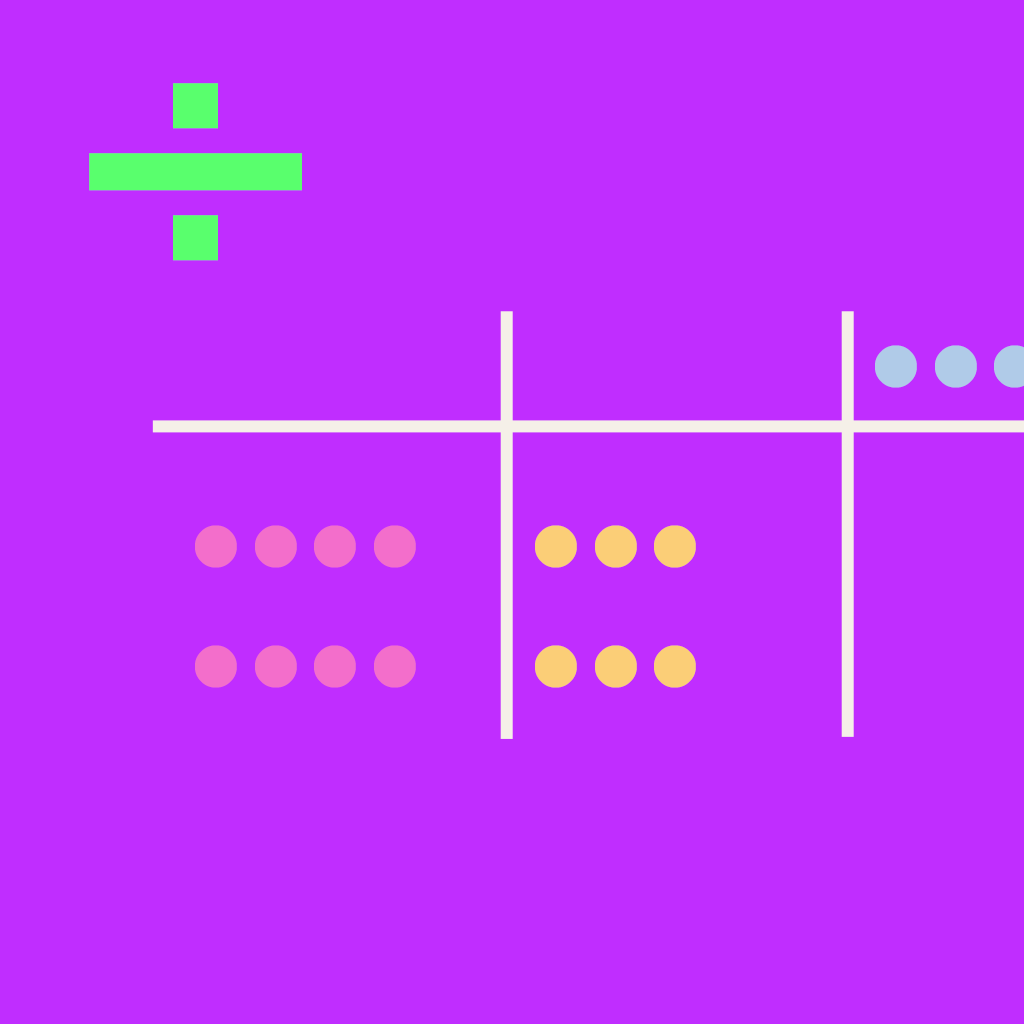
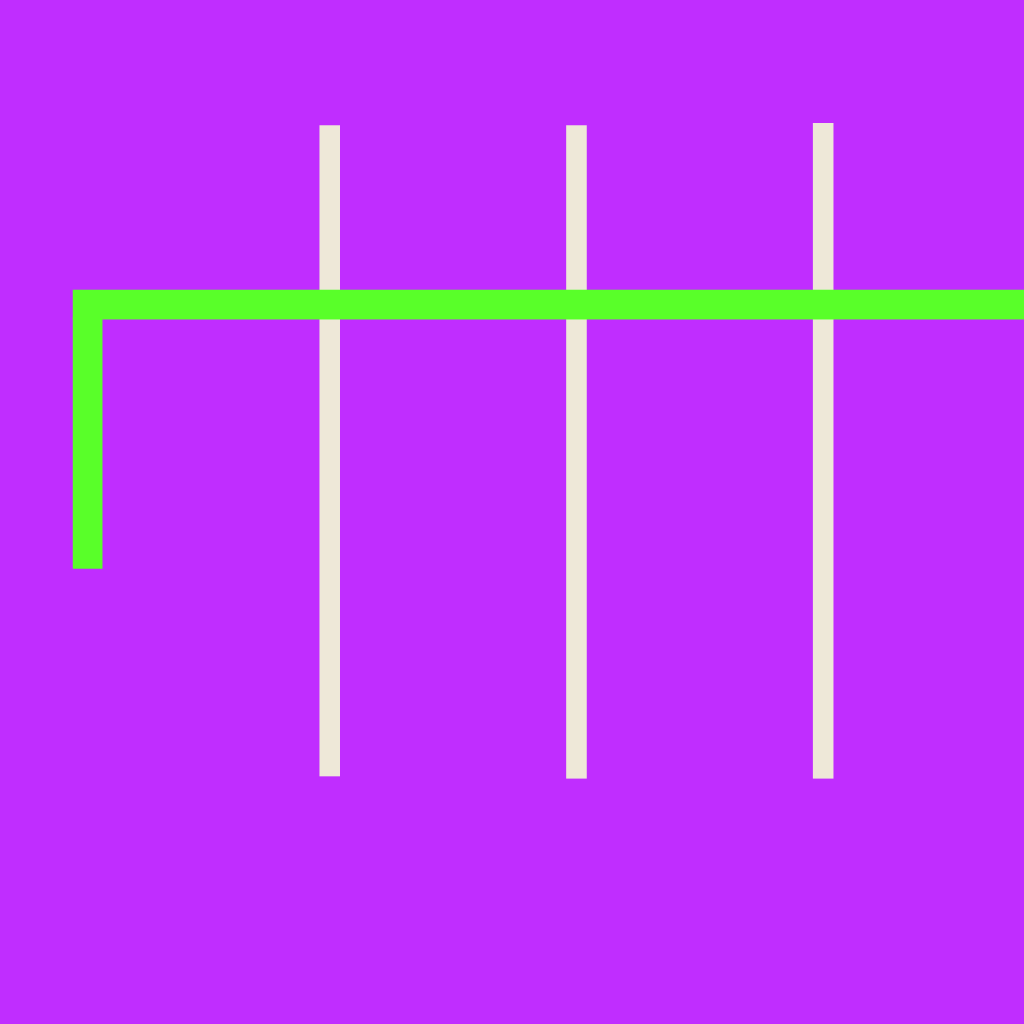
Column Division
The column division method is a simple variation of the traditional long division method. Lines are drawn to separate the digits of the divisor. Each place-value column is solved from left to right.
Everyday Column-Addition
The Everyday column-addition method was developed by a first grader. The method has two stages. In the first stage the digits are added one column at a time in each column. After the first stage some columns can have two-digit numbers. In the second stage the carries are done to obtain the result.
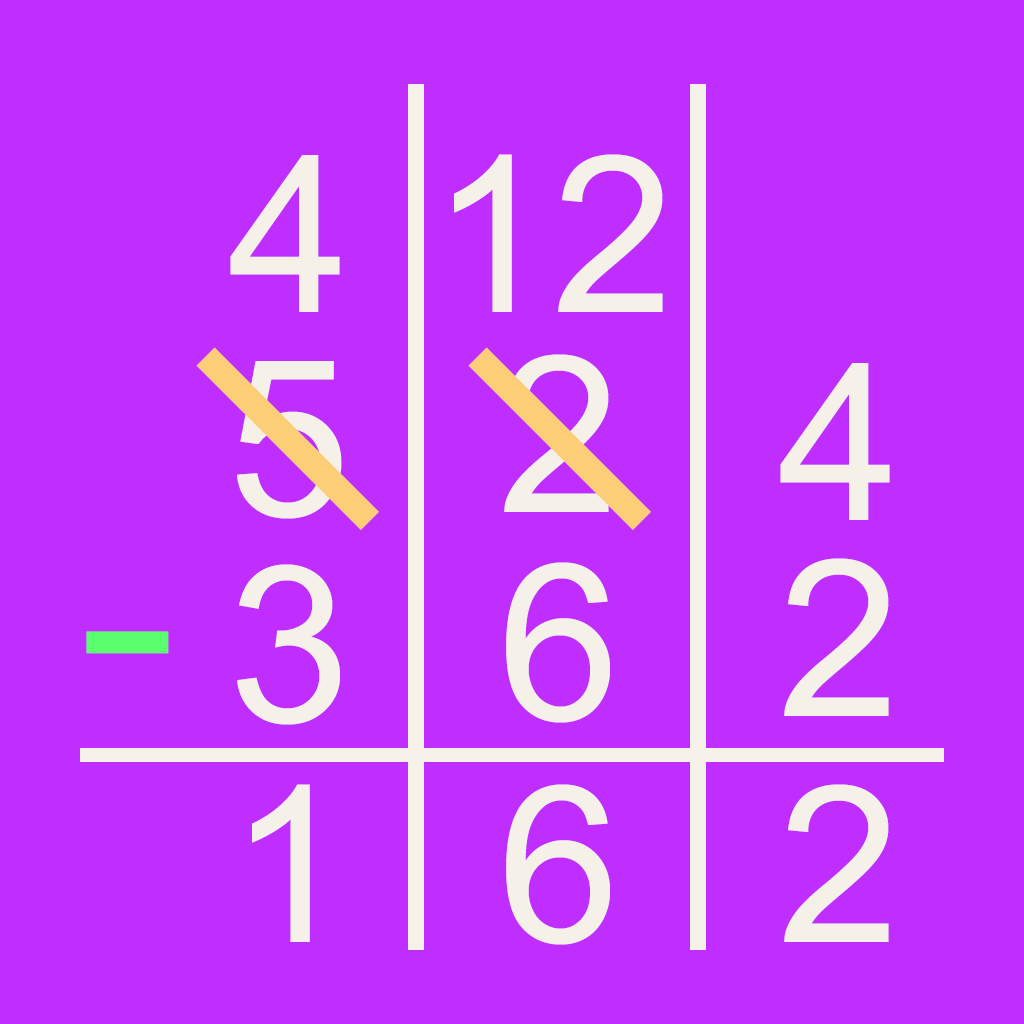
Partial Differences Subtraction
The partial differences subtraction method is a two-step process. In the example 936 - 580, each place value is first subtracted separately from left to right. The partial differences are added and 400 - 50 + 6 produces the answer 356.
Wired.com: “Esa Helttula’s apps are all fantastic for math learning and practice, and aren’t cluttered with mini-games, incentives, or annoying music.”
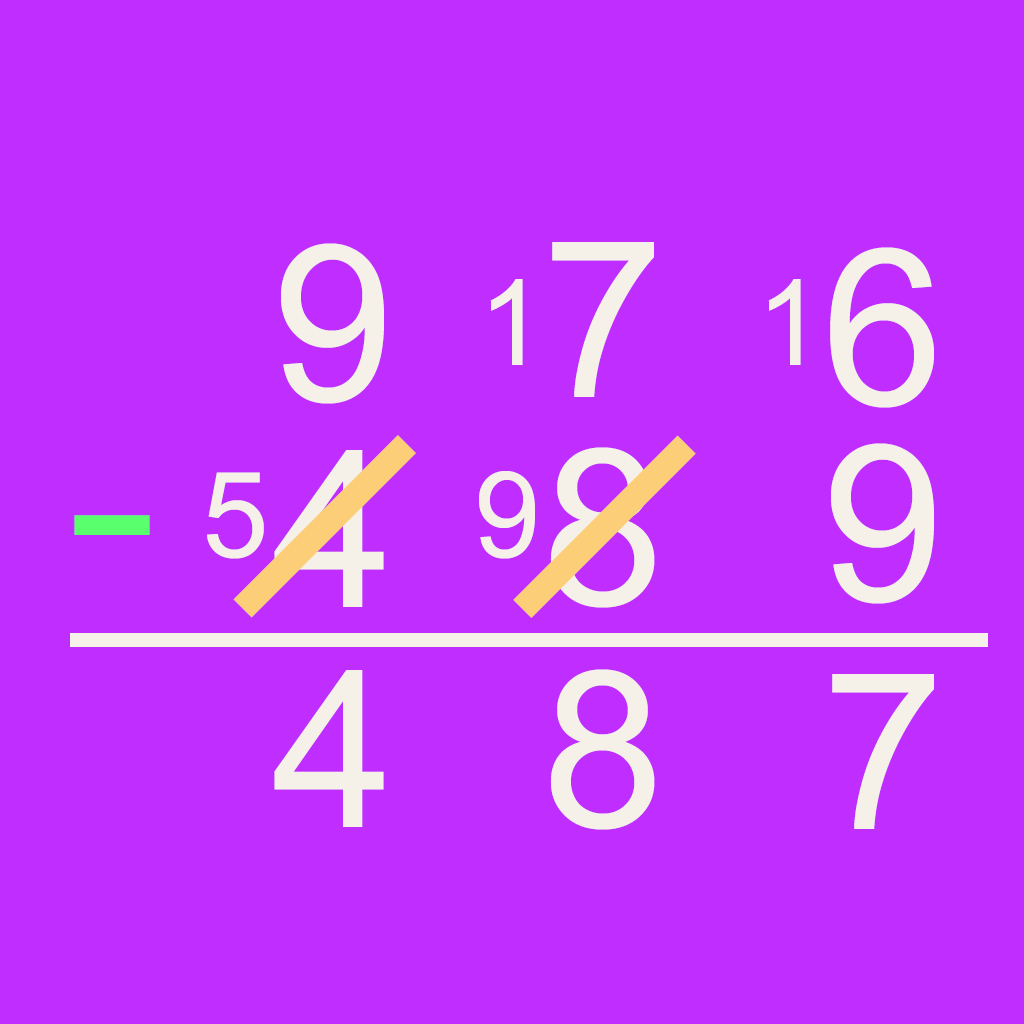
Trade-First Subtraction
The trade-first subtraction method is similar to the traditional column subtraction method. The method has two stages. All of the "trading" or "borrowing" is done first. Then the subtractions are solved. This gives the method it's name, "trade-first."
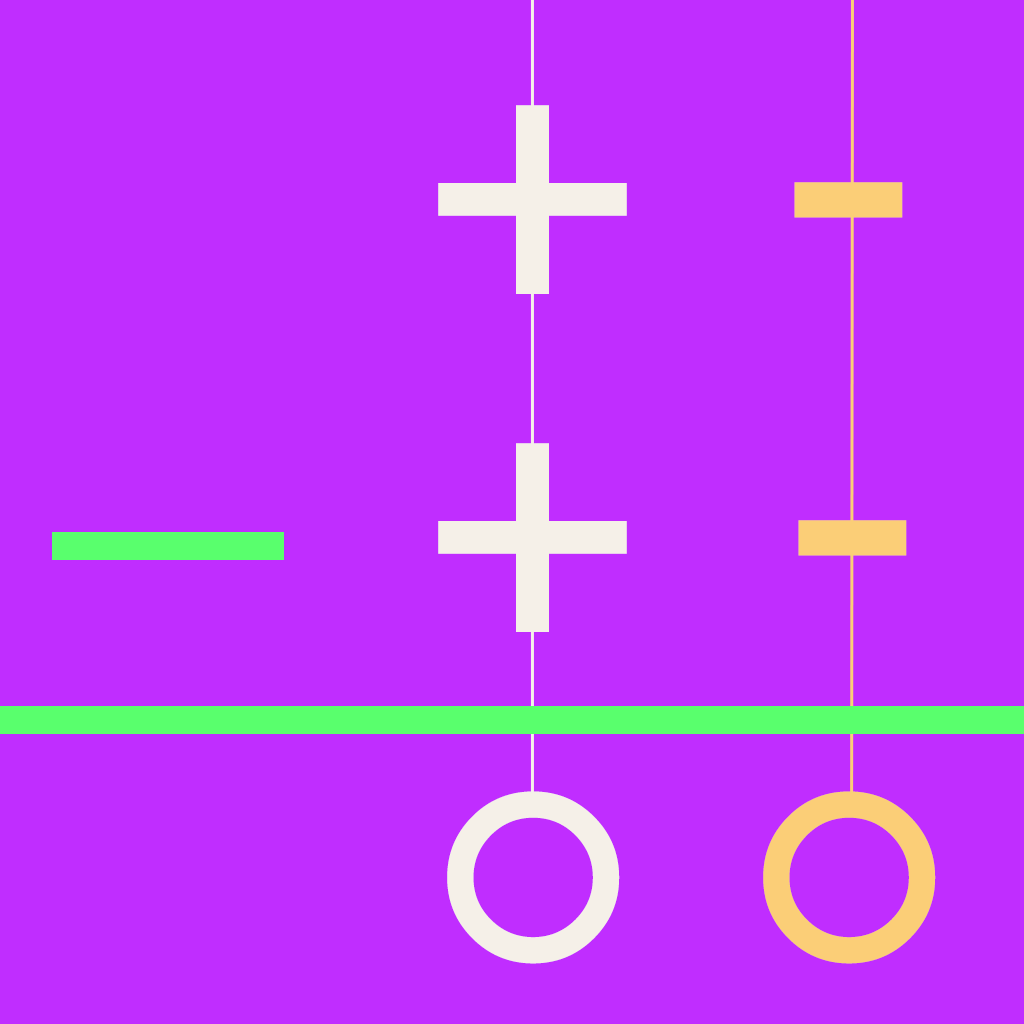
Equal Addition Subtraction
The method is based upon the idea that adding the same amount to two numbers will not affect the difference between the two numbers. The process can be thought as:
- Work column by column from right to left
- When the digit of the first number is smaller than the corresponding digit of the second number, add ten to the digit of the first number and one to the digit of the second number in the next column to the left.
The equal addition subtraction method is also called the ‘borrow and repay’ method or equal additions method for subtraction. Today the method is used in Australia and Latin America. The equal addition used to be a very popular method for subtraction in US until the middle of the 20th century.
Left-to-Right Subtraction
The left-to-right subtraction method is a two-step process. In the example 936 - 581, the number to be subtracted is first written in an expanded form: 500+80+1. Each of the parts is then subtracted from the starting number. In our example 936-500=436, 436-80=356 and finally 356-1=355.
Privacy
The apps have no ads or in-app purchases and they do not transmit any data during the operation of the app. The apps also do not contain any links to other apps or the web.
Videos
Dozens of videos of these and other apps can be found at idevbooks.com.}
Read more